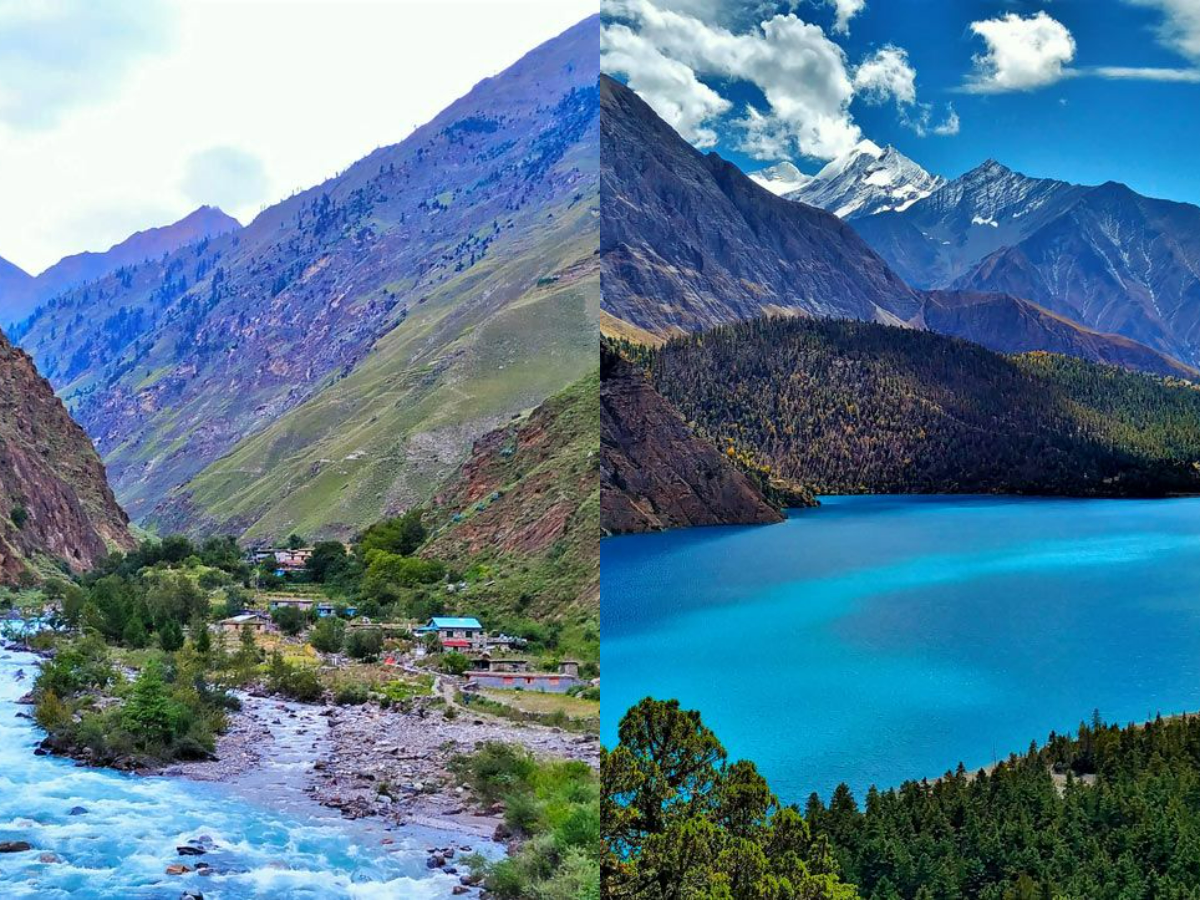
Shey Phoksundo National Park – the only trans-Himalayan national park
The local's main religion is 1800 years old Bon Buddhism Which is rooted from Animism and Buddhism. The origin of Bon-po religion is the western Tibet.
Shey-Phokaundo National Park (Nepali: शे-फोक्सुण्डो राष्ट्रिय निकुञ्ज) is the largest national park of Nepal. It’s has diverse terrain and altitude variation supporting wide range of vegetation and wildlife. The park was established in 1984 AD. The total area of a park is 3555 sq. km and the buffer zone covers 1349 sq. km area.
Location of Shey-Phoksundo
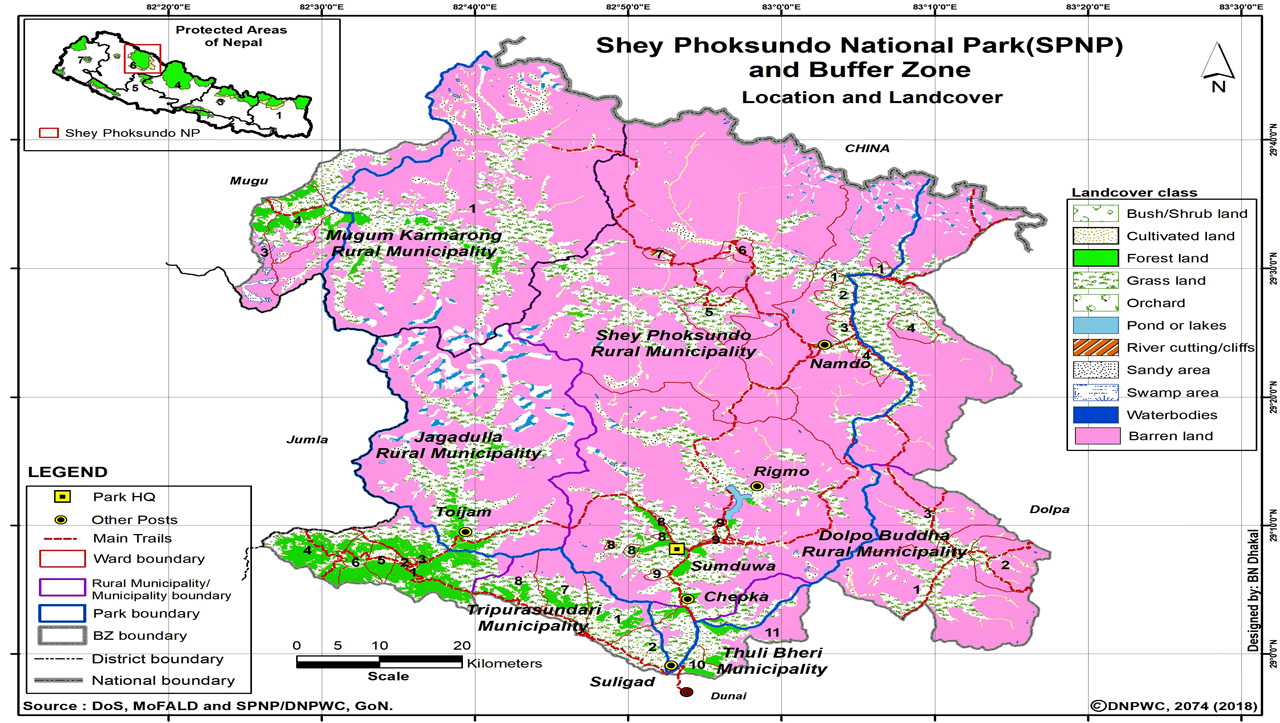
Shey-Phoksundo is spread over Mugu and Dolpa districts of northen-west Nepal in the trans-Himalayan region. The park area extends up to Nepal-Tibet border on the north where the Himalayan peaks guard it’s boundary with Tibet, China. Most of the park’s region lies in the north of Himalayan crest. The maps coordinates are of location are 29°21’29″N by 82°50’44″E.
Main Attractions of Shey-Phoksundo
- Kanjirowa Himal (काञ्जिरोवा हिमाल)
- Shey Monastery (शे गुम्बा)
- Shey Phoksundo Lake (शे फोक्सुण्डो ताल)
- Suligad waterfall (सुलिगढ/पाउली झरना)
- Langu Gorge (लङ्गु घाटी)
Key features of Shey-Phoksundo National Park
- The park has rare trans-Himalayan ecosystem. So diverse biotic system is an outcome of altitude variations and climatic difference.
- The park elevation ranges from 2130 m in Ankhe (आँखे) to 6889m; top of Kanjirowa Himal.
- There are many mountains of over 6000 m height. Among them Kanjirowa Himal is the popular one.
- Vegetation: It has 286 plant species of botanical importance. Lower part contains pine, willow oak, cypress and walnut. Further, the higher region has juniper, pine and birch plants. Alpine areas have wild rose, caragana and berberis.
- The upper elevation has barely any tress and is arid with alpine grasslands. Moreover, there is no vegetation above the ice line.
- Mammals: It is home to Himalayan thar, musk deer, marmot, sheep, mouse-hare, leopard, weasel, ghoral, lungur and rhesus monkey, jackal, Himalayan black bear etc. Most importantly the endangered show leopard appears rarely in the Park Mountains.
- Birds: There are over 200 birds species including Tibetan partridge, white-throated tit, yellow-throated martin, wood accentor, wood snipe, crimson-eared rose finch, cheer pheasant, chough, brown dipper, Impeyan, ravens, Himalayan griffon, Tibetan twit, Tibetan show cock, lammergeyer etc.
- Six species of reptile and 26 species of butterflies also live in the park.
- Shey Phoksundo Lake: It is the second largest and deepest lake of Nepal. The lake is located at an elevation of 3611.8 m above the sea level in southern region of upper region in Suligadh. It is famous for enticing turquoise color and mirror effect in its layer.
- Suligadh waterfall: The outlet from shey Phoksundo Lake forms suligad waterfall; the higest waterfall of Nepal.
- Rivers: Panjang, Namajung and Khung are the major rivers of the park. The Jugdual and Suligad rivers are main tributaries of the Langu River and the Thuli Bheri River respectively. The Langu River drains the east of Upper Dolpo region and flows westward.
- Climate: The massive barriers formed with Kanjirowa and Dhaulagiri Ranges act as a blockage to a wind thus making the trans-Himalayan region less rainy.
- The monsoon season in the region occurs from June to September. During monsoon the annual precipitation is 1500 mm in the south (Suligad) and about 500mm in the north.
- During much of the winter, the temperature in places above 3000 m drops below freezing points. Snowfall becomes frequent above 2500 m.
- Floras: Park’s forest covers less than 5% area and shelters 286 plant species of ethno botanical importance. The upper region in the north has plants like Rhododendron, Salix, white Himalayan birch, Caragana shrubs, Juniper, Silver fir etc. Mush of the forest is in southern region.
- The Suligad valley consist of Rhododendron, Silver fir, Hemlock, Blue Pine, Bamboo, Spruce, Cedar, Poplar etc.
- Mammals: Shey Phoksundo is a home of different endangered species like snow leopard, Musk deer, Ghoral, Himalayan thar, Jackal, Grey wolf, Leopard, Blue Sheep, great Tibetan sheep, Himalayan black bear etc.
- Birds: More than 200 species of birds live in the park including Yellow throated martin, Wood accentor, Tibetan partridge, White throated tit and crimson-earned rose finch.
- Six reptile species and 29 butterfly species including Paralasa nepalaica; the highest flying butterfly in the world, are found in the park.
- Settlement: Villages in the region are one of the highest settlements in the globe. The local’s main religion is 1800 years old Bon Buddhism Which is rooted from Animism and Buddhism. The origin of Bon-po religion is the western Tibet.
- Dho Tarap (4000 m) is the village in the Upper Dolpo region with dense population. It is considered the highest human settlement on the planet earth. Presence of small Gumbas, Mani stone walls, chortens and prayers flags throughout the village reflect that the cultural ambiance of Dho Tarap (धो ताराप) touched with Buddhism. The houses ar made from river stones with wooden windows and roofs of firewood. Dhoro are Maran are small villages above Dho Tarap. Maran is the last village before starting the ascent of Jhyarkoi La.
- Monasteries: The Park is sacred area and reaches in Gompas (Monasteries) and chortens. The Shey Gompa was built in 11th The 900 years old Thashung Gompa was built for wildlife conservation. Also, the two nearby monasteries from the Dho Tarap village are Shipchaur Gompa in Shipchowk and Ribo Bhumpa Gompa on the right.
- Thanka Paintings: Tibetan Buddhist paintings on cotton cloths are additional attraction of this place.
- Ringmo (रिङ्गो) Village located inside park area is a traditional Tibetan village which sits on the landslide dam of Phoksundo Lake. The locals of Ringmo village are devotee of Bonpo religion; the foundation of Tibetan Buddhism. There are glaciers and waterfall nearby this village.
- Other main village inside the park Salclnag, Tatgaun, Pugmo and Kagun. In addition some of the local towns are Dunai, Sangta and Chhepka where local lodge accommodations are available.
- There are ancient local routes in this region which were once a salt trade caravans, now a trekking trails, between Nepal and Tibet.
- The park offices are present Suligad, Chhepka, Toijen and Palam Ringmo. Moreover there is a park headquater in Palam, Dolpa district.
- Shey Phoksundo Lake separates the Lower Dolpo and the Upper Dolpo region being itself to the Lower Dolpo region. Both the regions, being the off the beaten surreal destinations, are famous for trekking.
- Lower Dolpo is the permitted for individual trekking and group trekking, the trek goes up to Ringmo or Phoksundo Lake.
- Upper Dolpo is the restricted are which is permitted for group trekking only, It requires to get special permit which can be arranged through any trekking agency of Nepal.
- The popular passes in the Phoksundo region are Leti Lagna (3385 m), Bharbhare Lagna (4297 m), Kagmara La (5115 m), Bagala La (5169 m) and Numala La South (5309 m).
How to reach Shey Phoksundo National Park?
- Road transportation: The Park is 317 km away from Kathmandu; the capital city. The overland route ton park goes along Kathmandu – Khalanga, Jajarkot – Raadee – Tallu Bagar – Suligadh.
- Air transportation: Fly Kathmandu – Nepalgunj – Juphal Airport, Dolpa. The park entrance at Suligadh is half day walk away from Juphal Airport.
- Air transportation: Fly Kathmandu – Nepalgunj – Jumla Airport, Jumla. Cross Til Khola and Chaudabise Khola to reach Gothi Chaur.
Additional Information
Activities: Trekking, mountaineering
Accommodation: Camping, local lodge (Camping only in Upper Dolpo region)
Access: Fly Kathmandu – Nepalgunj (about 1 hour). Fly Nepalgunj – Juphal Airport, Jumla (20 minutes). Walk for 5 to 6 hours to Suligadh.
Best Season: Spring (March – May) and autumn (September – Octomber)
Park Headquarter: Sumduwa, Palam
